PeekMed
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Orthopedic Decision-Making rapidly transforms the medical landscape, particularly in orthopedics. For orthopedic surgeons, fellows, and residents, understanding the implications of this technology is essential. Artificial Intelligence can enhance diagnostic precision, tailor treatment protocols, and improve patient care. However, using Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making also carries risks that must be managed effectively.
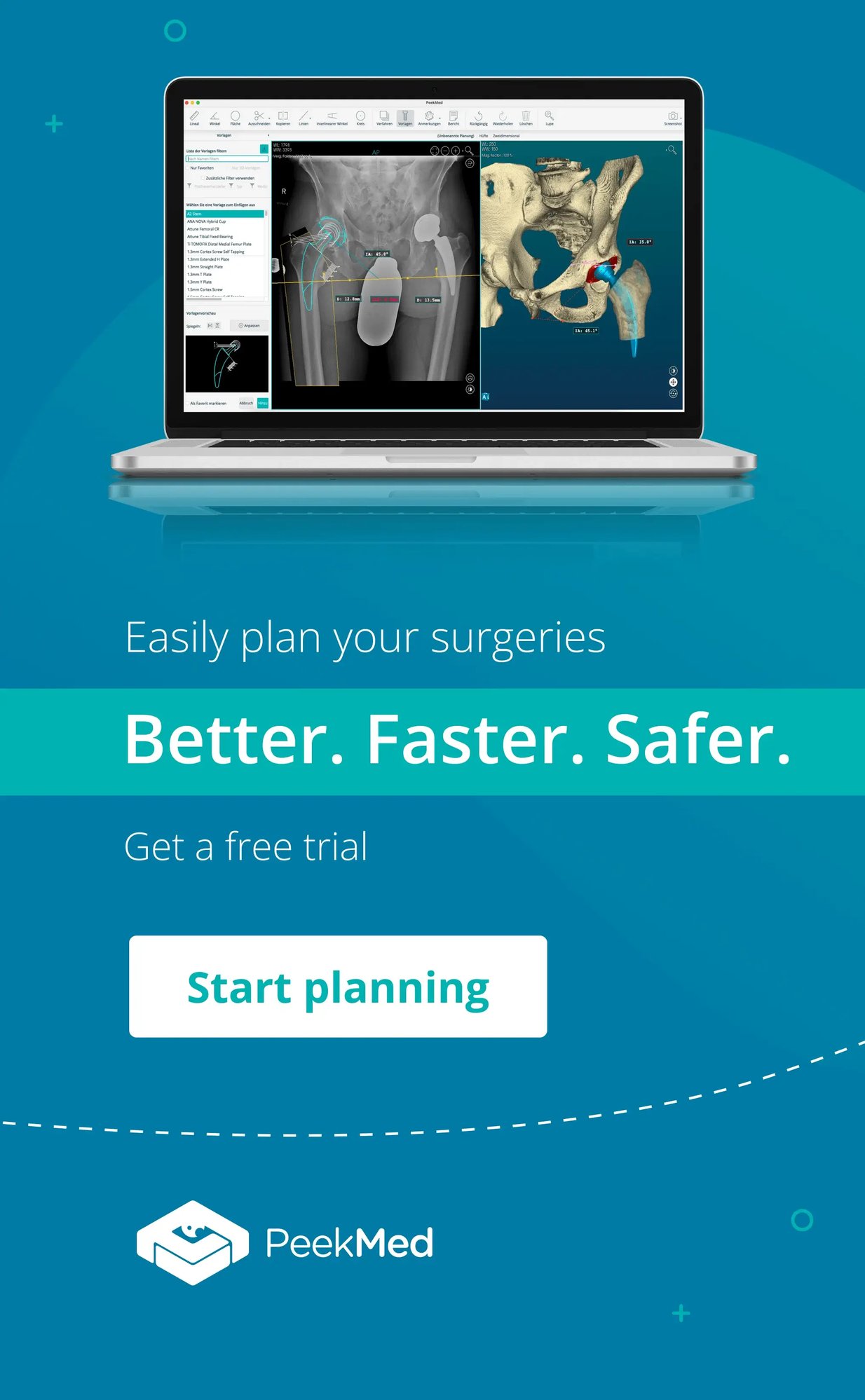
In orthopedics, accurate decision-making is crucial for successful patient outcomes. With tools such as machine learning and neural networks, Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making aids in diagnosing conditions and predicting postoperative results. By minimizing human error and optimizing treatment strategies, AI allows surgeons to dedicate more time to complex cases.
Table of Contents:
Key Benefits of AI in Orthopedic Decision-Making
Risks Associated with AI in Orthopedic Decision-Making
Navigating the Risks and Benefits
Key Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making
Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
Algorithms in Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making excel at interpreting imaging studies. They can detect subtle anomalies in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, leading to improved diagnostic accuracy and timely interventions.
Personalized Treatment Solutions
By analyzing extensive patient data, Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making can formulate personalized treatment plans. This results in tailored recommendations that consider individual patient histories, improving treatment outcomes.
Predictive Analytics Capabilities
The predictive analytics features of Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making can forecast patient recovery trajectories and complications. This allows orthopedic surgeons to proactively manage potential postoperative issues.
Risks Associated with Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making
Algorithmic Bias
A significant concern in Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making is algorithmic bias. If the training data lacks diversity, it can lead to skewed results that affect diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Dependence on Technology
The growing reliance on Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making may risk undermining surgeons' clinical judgment. AI should supplement—not replace—human expertise.
Data Security and Privacy
The necessity for large datasets in Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making raises privacy concerns. Ensuring robust data protection measures is crucial to safeguard sensitive patient information.
Navigating the Risks and Benefits
Collaborative Integration
Successful application of Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making will likely require collaboration between AI and healthcare professionals. By automating routine tasks, AI allows surgeons to focus on complex clinical evaluations.
Ongoing Education
Continuous education in Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making is vital for surgeons. Understanding AI's functionality and limitations can help mitigate over-reliance on these systems.
Ethical Standards
Establishing ethical guidelines for Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making is essential to promote responsible use. These guidelines should emphasize data integrity and transparent decision-making processes.
Investing in Data Security
As the integration of Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making expands, robust data security is non-negotiable. Ensuring patient confidentiality through encryption and secure data practices is imperative.
Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedic Decision-Making offers substantial benefits, including improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized care, and effective predictive analytics. However, these advantages come with significant risks, such as algorithmic bias and data privacy concerns. A balanced approach that integrates human expertise with Artificial Intelligence can enhance patient outcomes and elevate the quality of orthopedic care.