Going beyond ChatGPT: How Data Augmentation is reshaping Orthopedics
Data augmentation is revolutionizing orthopedics by enhancing diagnosis, treatment, and research through advancements in technology and deep learning.
By enhancing and expanding datasets, orthopedic surgeons can unlock valuable insights and drive innovation. In this article, we will delve into the concept of data augmentation, explore the differences between augmented and synthetic data, and highlight the diverse applications and benefits it offers within the realm of orthopedics.
What is Data Augmentation?
In the digital age, data has become the cornerstone of innovation across various domains. Data augmentation is a process that involves manipulating existing data to generate variations of the original data, thus enlarging the dataset. These variations are designed to capture different aspects, perspectives, or conditions present in real-world data.
This process aims to introduce diversity and increase the amount of information available for the analysis and training of artificial intelligence algorithms and machine learning models. This also helps to identify patterns and trends that would otherwise go unnoticed.
What is Synthetic Data? And Augmented Data?
Before delving into the applications and benefits of data augmentation procedures, let's distinguish between augmented and synthetic data.
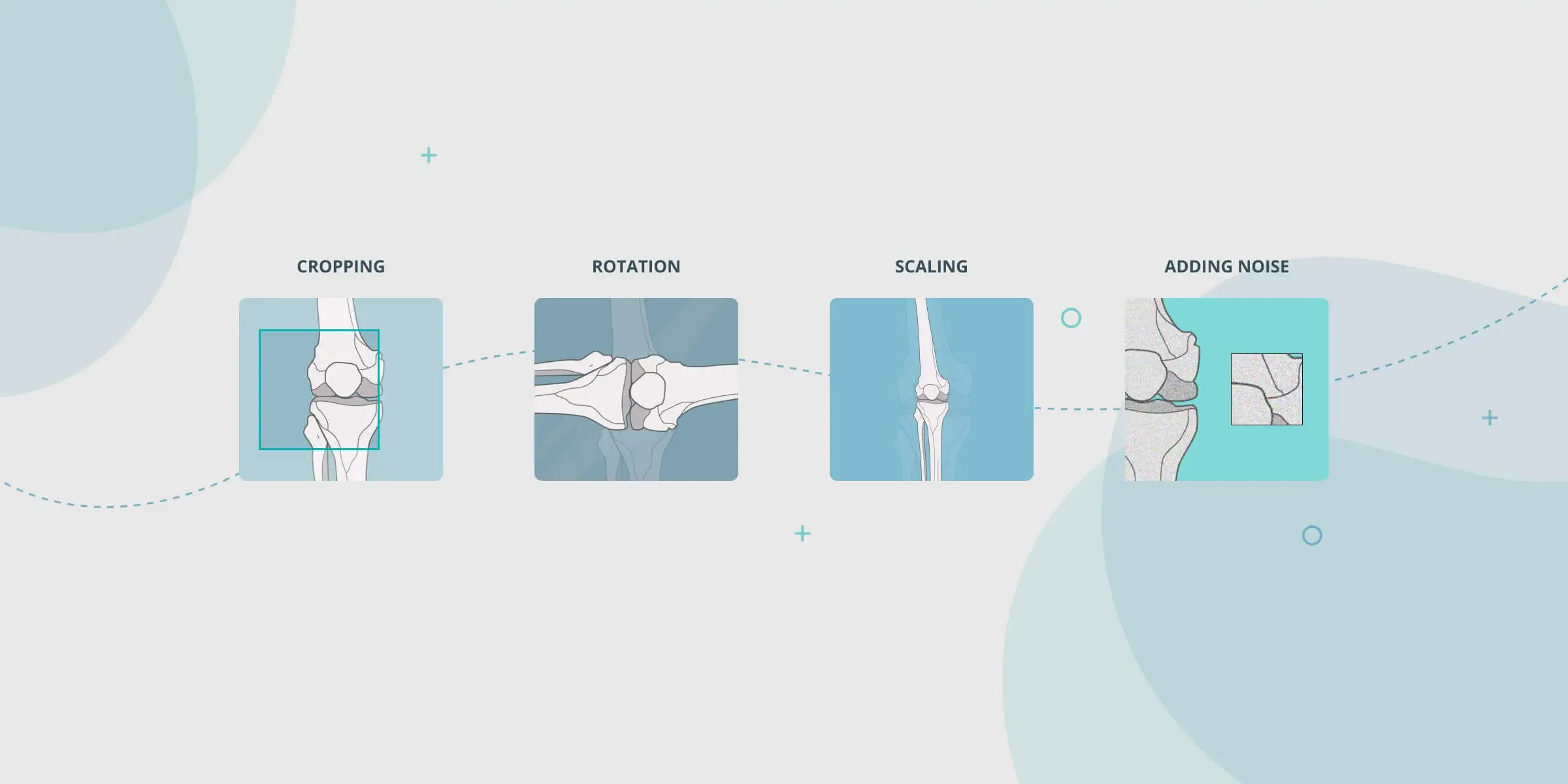
Augmented data refers to the process of enhancing existing datasets through various techniques, such as image manipulation, cropping, rotation, scaling, or adding noise. These alterations generate additional variations of the original data while preserving its authenticity.
On the other hand, synthetic data involves generating entirely new data from scratch that imitate real-world samples. This can be achieved through generative models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
.jpg?width=2400&height=1400&name=Data%20Augmentation%20(1).jpg)
In orthopedics, augmented data is particularly valuable because it can help to capture variations in patient anatomy, pathology, and demographics that are relevant to the field.
Benefits of Data Augmentation in Orthopedics
By expanding and enhancing existing datasets, data augmentation offers a myriad of benefits that empower orthopedic surgeons, researchers, and implant manufacturers to unlock new insights, optimize treatment strategies, and elevate patient care.
Let’s list some of the benefits:
-
Data Anonymization
Anonymizing patient data is crucial to protect privacy and adhere to ethical standards. By applying methods such as image blurring, pixelation, or perturbation, it is possible to conceal patient identities while maintaining the integrity and patterns required for analysis. Data augmentation allows researchers to work with larger, diverse datasets, ensuring privacy compliance and accelerating advancements in orthopedic research and care.
-
Improved Generalization
Data augmentation allows models to generalize better by exposing them to a broader range of variations. By augmenting datasets, orthopedic surgeons and researchers can ensure their algorithms are more robust and capable of handling diverse patient populations, different imaging conditions, and rare pathological cases.
-
Enhanced Performance
Augmented data helps overcome the challenges of a limited sample size. With a larger and more diverse dataset, orthopedic models can achieve higher accuracy, better precision, and reduced overfitting. This translates into more reliable diagnostic tools and improved surgical planning.
-
Cost and Time Efficiency
Generating augmented data can be an alternative to collecting new data. Traditional data collection methods can be labor-intensive, expensive, and often limited by ethical considerations. The number of patients needed for clinical trials can be reduced or even eliminated as researchers can simulate the effects of different interventions and implant designs without having to conduct actual trials.
Applications of Data Augmentation in Orthopedics
Now, let’s dive a little bit deeper into the world of Data Augmentation and understand the tangible applications these techniques can have in the practice of orthopedics:
-
X-ray Image Augmentation
X-ray images play a pivotal role in orthopedic diagnosis. By augmenting X-ray datasets, orthopedic practitioners can simulate different angles, zoom levels, and noise levels, or even apply super-resolution techniques to enhance image quality. This augments the dataset with additional variations that closely resemble real-world imaging conditions, enabling more robust model training.
-
Pathology Simulation
Augmenting data to mimic rare or complex pathological conditions can greatly enhance the capabilities of orthopedic models. By introducing synthetic abnormalities or deformities in X-ray images, surgeons and implant manufacturers can develop algorithms that aid in accurate detection, preoperative planning, and implant design.
-
Diagnostic Support
Augmented data aids in the accurate and efficient diagnosis of orthopedic conditions. By incorporating variations of X-ray images, algorithms trained on augmented data can assist in detecting fractures, joint abnormalities, and other pathologies. This supports orthopedic surgeons in making timely and precise diagnoses, leading to improved patient management.
-
Surgical Planning and Intervention
Augmented data enables orthopedic surgeons to enhance their preoperative planning and decision-making processes. By analyzing a diverse dataset of X-ray images, CT scans, and patient records, surgeons can identify patterns, predict treatment outcomes, and customize surgical approaches accordingly. This empowers them to optimize surgical interventions and minimize risks for better postoperative results.
-
Implant Design Optimization
Data augmentation can help refine implant designs, enhancing their compatibility with patients' unique anatomies. By leveraging augmented data, implant manufacturers can simulate various scenarios and evaluate the performance of new designs. This iterative process improves implant efficacy, longevity, and patient satisfaction.
While these applications appear promising, a valid question arises: can augmented and synthetic data be trusted? A study developed at the University of Jyväskylä's Digital Health Intelligence Laboratory concluded that medical experts were unable to differentiate between real and synthetic x-ray images of knee osteoarthritis proving the quality of the images artificially generated.
How does PeekMed use Data Augmentation?
PeekMed strives to keep up with the latest technologies in Artificial Intelligence, including data augmentation. We use data augmentation as a strategy for segmenting medical images, X-ray image augmentation, and surgical planning which aids in improving our system and the whole experience surgeons have while interacting with it.
As we look towards the future, the integration of data augmentation can enable predictive analytics, revolutionizing how orthopedic professionals approach treatment planning, implant design, and postoperative care. X-ray images are just one example of the types of data that can be used for data augmentation in orthopedics, and the possibilities for this technique are endless.
Embracing data augmentation is not only a means to stay at the forefront of medical innovation but also a commitment to providing the best possible care for orthopedic patients worldwide.

