PeekMed
In the world of orthopedic surgery, precision is paramount. Surgeons rely on advanced tools and technologies to ensure accurate procedures and optimal patient outcomes. One such advanced technology is orthopedic navigational technology, which is still evolving, looking for the best match between innovation and clinical needs.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of orthopedic navigational technology and explore its potential to transform the field of orthopedics and robotic surgery.
Understanding Orthopedic Navigational Technology
To better comprehend its importance, let's start with the navigation system definition. Orthopedic navigational technology refers to the integration of surgical navigation systems and robotic assistance in orthopedic procedures.
It encompasses a range of advanced imaging, computer-assisted planning, and intraoperative guidance systems designed specifically for orthopedic surgical procedures.
These systems combine cutting-edge technologies to provide real-time guidance and precise navigation during surgeries, enhancing the surgeon's ability to perform complex maneuvers with utmost accuracy.
The Role of Orthopedic Navigational Technology in Surgical Planning
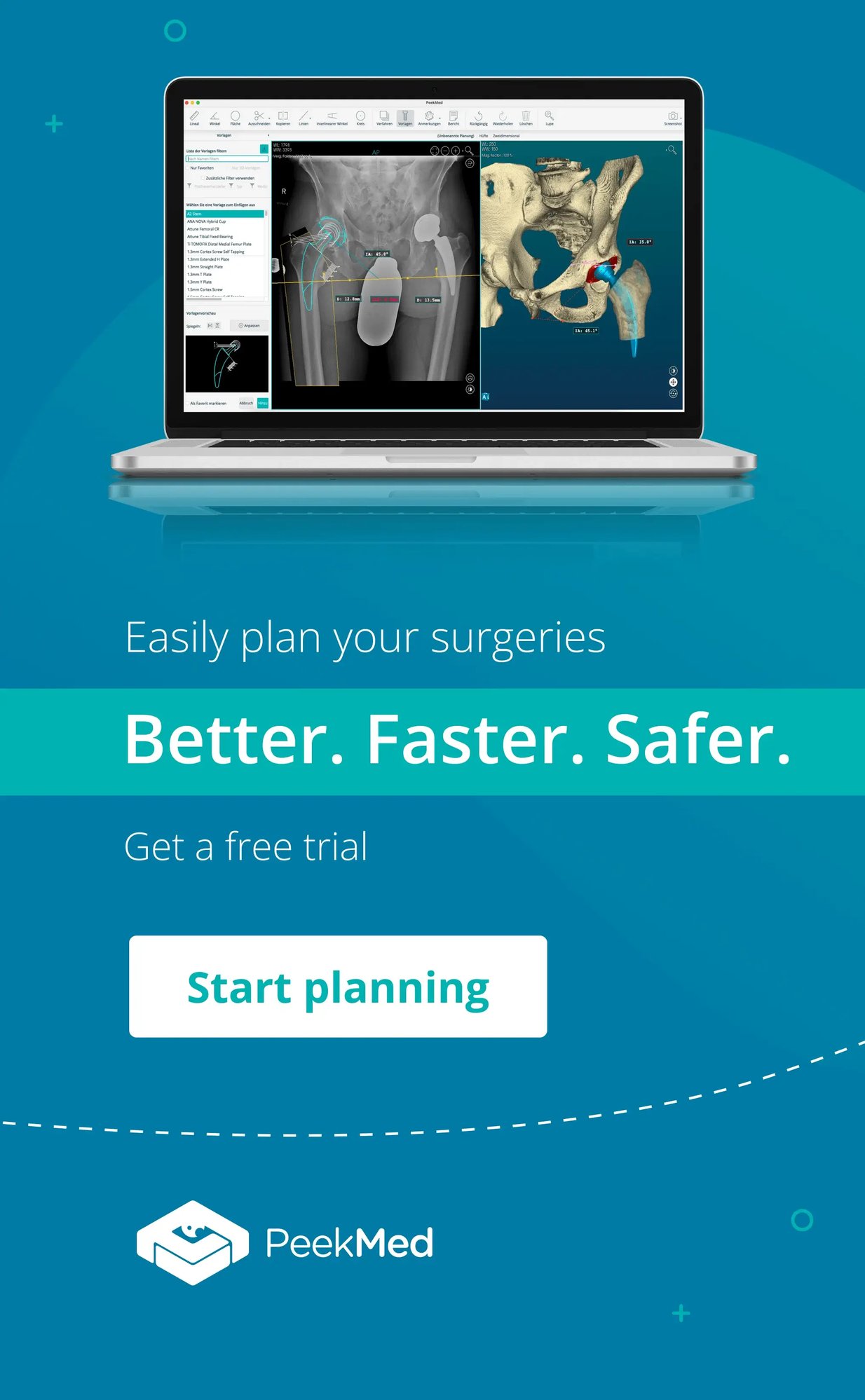
Orthopedic navigational technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing surgical planning. Surgeons can use preoperative imaging data, such as CT or MRI scans, to create three-dimensional models of the patient's anatomy.
These models allow for a detailed evaluation of the bone structure, joint alignment, and biomechanical factors, aiding in the development of personalized surgical plans tailored to each patient's unique needs.
Surgeons can then use this model to plan their approach, identify optimal trajectories, and make precise adjustments during the procedure.
Real-Time Guidance during Orthopedic Surgeries
During orthopedic procedures, navigational technology provides real-time guidance to surgeons, ensuring optimal implant placement, precise bone resection, and alignment.
By tracking instrument positions relative to the patient's anatomy, navigational systems provide visual feedback, allowing surgeons to make informed decisions and adjust their techniques as needed. This dynamic guidance enhances surgical accuracy, reduces the risk of errors, and ultimately leads to improved patient outcomes.
Benefits of Orthopedic Navigational Technology
The adoption of orthopedic robots and navigational technology brings forth a myriad of benefits for both surgeons and patients. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
-
Improved Precision
This technology offers enhanced dexterity and precision, complementing the surgeon's skills, which allows the surgeon to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy, even in challenging anatomical regions.
-
Minimally Invasive Surgeries
By providing surgeons with real-time feedback and accurate visualization, this technology allows smaller incisions to be made, resulting in reduced tissue trauma, less postoperative pain, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times.
-
Enhanced Safety
The integration of navigational technology improves patient safety by providing real-time feedback, ensuring accurate implant placement, and minimizing the risk of complications.
-
Streamlined Workflows
Orthopedic navigation systems facilitate efficient surgical workflows by offering seamless integration with other technologies, enabling precise instrument tracking, and optimizing resource utilization.
-
Enhanced surgeon training/expertise
This technology provides a platform for preoperative planning and simulation, allowing surgeons to practice procedures in a virtual environment which improves their decision-making skills during surgery.
Also, the implementation of navigational technology can streamline healthcare delivery. As said previously, this technology can potentially shorten hospital stays and decrease post-operative rehabilitation periods. This, in turn, can alleviate the burden on healthcare systems, improve resource allocation, and enhance patient satisfaction.
Applications of Orthopedic Navigational Technology
By minimizing errors in implant positioning and alignment, navigation technologies can reduce the need for revision surgeries and improve long-term functionality. This level of precision is especially crucial in delicate procedures where even minor deviations can have significant consequences.
Orthopedic navigational technology finds application in various surgical procedures, including:
-
Joint Replacement Surgery
In joint replacement procedures, navigational technology aids in precise implant positioning, alignment, and balancing of soft tissues. This leads to improved joint stability, reduced implant wear, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, and faster patient recovery.
-
Spine Surgery
Navigational technology assists in the accurate placement of pedicle screws, facilitating spinal fusion procedures, and correcting complex deformities. Surgeons can navigate intricate spinal anatomy with greater precision and safety, resulting in improved patient outcomes and reduced complications.
-
Orthopedic Trauma Surgery
Orthopedic navigational technology enhances the management of complex fractures by enabling precise alignment and optimal implant positioning. This technology assists surgeons in achieving anatomically correct reduction, facilitating faster healing and improved functional recovery.
-
Sports Medicine
In sports medicine procedures, orthopedic navigational technology aids in accurate tunnel placement during ligament reconstruction surgeries, optimizing graft fixation and improving surgical outcomes for athletes.
Embracing the Future of Orthopedic Navigational Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of orthopedic navigational technology holds immense potential. Advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotic-assisted systems are poised to further enhance the capabilities of navigational technology, enabling even more precise interventions and better patient outcomes.
While orthopedic navigational technology holds tremendous promise, it is important to recognize that they are still in the early stages of adoption. Surgeons interested in these technologies should stay abreast of the latest advancements and collaborate with manufacturers and research institutions to further refine and develop these orthopedic surgical tools.