-Jul-28-2022-09-34-57-27-AM.png)
Total Hip Arthroplasty (THA): from planning to performing
As you know, total hip arthroplasty (THA) – often referred to as traditional hip replacement surgery or hip arthroplasty – is normally used to resolve issues related to hip pain and stiffness.
However, while it is a very common procedure, THA is still a delicate technique. Errors might cause issues that lead to the need for limb lengthening and shortening surgery (longer leg and shorter leg) and damaged joints.
Surgical planning is a great strategy to prevent these episodes and is highly recommended to achieve correct and personalized hip replacement.
Preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty allows orthopedic surgeons to predict the optimal implant position and size. On top of that, surgeons gain insights into difficulties and issues that might appear.
But what has changed in the past years and how can technology improve how a THA is planned?
In the past, the most common approach would be to use acetate on a printed radiograph. Thankfully, technology brought us digital templating, not only making the whole process faster and automated but safer and more consistent.
This leads us to templating.
Total hip arthroplasty (THA) templating: What is it and why you should use it?
THA templating has been pointed out as a quick win for total hip arthroplasty techniques and a fundamental for the THA implant. Why? As you know, bone and cartilage are essentially what is replaced in a total hip replacement.
Templating allows the surgeon to do a preoperative physical examination and analysis. Thus the surgeon gains insights into the patient’s gait, hip range, and ipsilateral knee status.
Hence, when selecting the THA implant to be used, the orthopedic surgeon can consider not only the size of the said implant but also cut and move the fragments to know the surgery’s final result.
This improves the accuracy of the procedure.
A skillfully performed THA considers all 3 dimensions (3D) and preoperative planning software makes this much easier, too.
PeekMed allows you to import data from your imaging technologies and analyze the patient-specific anatomy in both 2 and 3D – or even simultaneously.
Digital templating also gives the surgeons more insights into all the opportunities available.
Instead of having to remember every implant manufacturer and size from memory, artificial intelligence (AI) will allow the surgeon to find what an arthroplasty procedure most indicated implant.
This process is automatic and takes only a few clicks. However, it takes into account patient anatomy and specific deformities to suggest the best possible treatment options.
In the following topic, we will explore how orthopedic surgeons can use this powerful tool to improve clinical outcomes.
A step-by-step approach to templating in total hip replacement
Before you even enter the Operating Room (OR), there are several essential pieces of information on how you do hip templating.
These should be taken into consideration for the best results:
1. Limb length discrepancy (LLD):
The transischial line is used to measure any leg length difference. Limb length discrepancy up to 1 cm is well tolerated;
2. Center of rotation:
The anatomical center of rotation of the femoral head should be reproduced by the position of the acetabular component. Acetabular and femoral component positioning should mimic normal anatomy.
The distance from the center of the femoral head to the teardrop (or another identifiable landmark) should be equal bilaterally. Excessive lateral positioning of the acetabular component increases the risk of dislocation and may cause limping and leg length discrepancies.
3. Femoral offset (FO)
When planning for a total hip arthroplasty a common mistake might be not taking into account the femoral offset.
Femoral offset is the distance from the center of rotation of the femoral head to a line dissecting the long axis of the femur.
In case the patient has an implant, the femoral offset is considered the distance from the center of rotation of the femoral head to a line bisecting the long axis of the stem.
A normal femoral offset is about 30 mm and 60 mm.
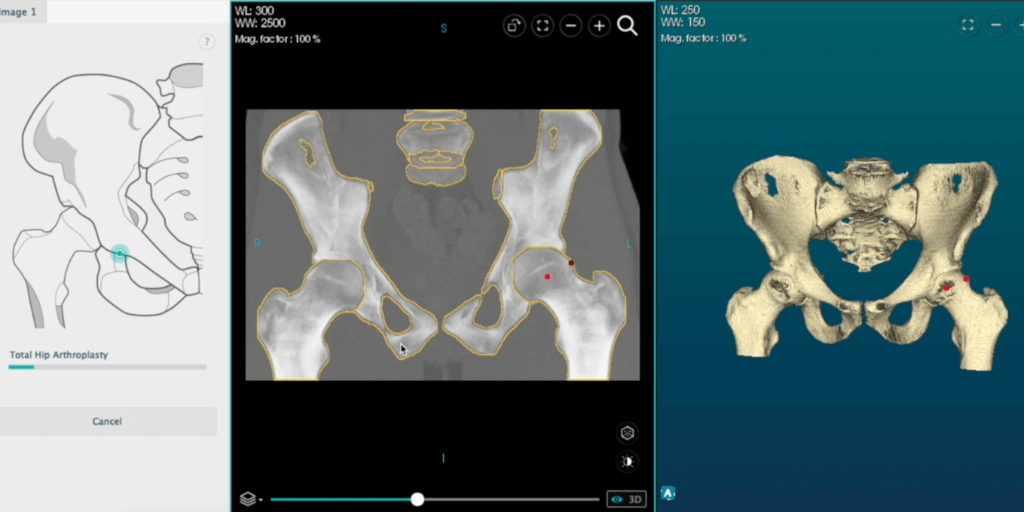
How to perform Total Hip Arthroplasty automatically
Using the hybrid environment with a CT scan, it is possible to perform automatic templating for hip arthroplasty. The desired implants are placed based on the previously defined landmarks in the procedure.
Firstly, you should perform a cut of the femur – or select a femur already cut.
The automatic templating detects the cup that better matches the femoral head diameter and places it in the planning view, which you can adjust on the configuration window. Besides, you can simulate the acetabular reaming according to the positioning of the cup component.
Then, based on the cup component, the compatible insert and the femoral head are added and automatically repositioned.
Proximal femoral resection and alignment of the cup, liner, head, and stem components were performed in real-time.
-2-2.png?width=1024&name=Untitled%20design%20(16)-2-2.png)
Total hip arthroplasty replacement protocol: promoting a safe recovery
Patient recovery is a pillar stone of a Total Hip Arthroplasty. While visiting a physical therapist after surgery is the common go-to solution, a THA recovery protocol is highly recommended to promote recovery without restraint.
Recommendations to give patients after THA Surgery:
-
Attend physical therapy 2-3 times a week for the first 6 weeks.
-
Avoid hip flexion over 90º degrees.
-
Crossing legs is a common position for many patients, this might lead to patients going beyond the neutral positions.
-
Sitting on low and soft surfaces is not recommended.
-
Caution with weight-bearing is also to be advised. While the patient should be putting some weight on the operated side, cautions should be made and in the first weeks, assistive devices should be considered.

