PeekMed
Artificial Intelligence is no longer a distant concept—it’s a clinical reality.
Surgeons, radiologists, and medical professionals around the world are already experiencing the shift. From preoperative planning to diagnostic imaging, AI has become a reliable assistant in the care process. But while terms like “AI in healthcare” are often used generically, the landscape is evolving, and with it, the language we use to describe it.
In this article, we’ll explore a more specific, more impactful term: Clinical AI.
We’ll unpack what it means, how it differs from broader Healthcare AI, and why this distinction matters for medical professionals, especially those in high-precision fields like orthopedic surgery.
We’ll also show you how tools like PeekMed are helping define this new category of AI that lives at the point of care.
By the end, you’ll clearly understand how Clinical AI originated, what makes it distinct, and how it’s being applied across diagnostics, planning, and surgical workflows—alongside helpful resources and internal articles that dig even deeper. Let’s break down.
What is Clinical AI?
In simple terms, Clinical AI refers to artificial intelligence technologies that assist directly in clinical decision-making, diagnosis, and patient-specific treatment.
It is not the AI that helps with appointment booking, hospital inventory, or health insurance claim processing. Rather, Clinical AI is what surgeons use to interpret medical imaging, simulate outcomes, and guide interventions. It’s what radiologists rely on to flag abnormalities in CT scans, and what mental health clinicians may use to screen for depression based on language and tone.
Unlike broader Healthcare AI, which addresses administrative efficiency and systemic logistics, Clinical AI operates within the patient care process itself, often at critical touchpoints where precision and accuracy are essential.
A Look Back: How the Term “Clinical AI” Emerged
The term “Clinical AI” emerged from a growing need to distinguish AI applications that influence medical outcomes from those focused on operational efficiency. Academic literature and digital health innovators began carving out this distinction in the late 2010s, as machine learning algorithms matured beyond experimentation and started delivering real-world value in diagnostics and care.
Organizations like Aidoc and Limbic have helped define the field, while healthcare policy bodies such as the European Commission now actively distinguish “clinical-grade AI” from more generalized healthcare technologies.
The reason?
Clinical AI requires a higher standard. It must be evidence-based, rigorously validated, and ethically applied—because it’s used at moments that directly affect patient lives.
Clinical AI vs. Healthcare AI
To better understand the distinction, let’s place both terms side-by-side:
|
Healthcare AI |
Clinical AI |
|
|
Scope |
Broad; includes clinical and non-clinical tasks |
Narrow; focused on clinical decision-making |
|
Key Applications |
Hospital management, EHR automation, billing |
Diagnosis, treatment planning, image analysis |
|
End Users |
Hospital admins, IT teams, policymakers |
Surgeons, radiologists, physicians, clinical teams |
|
Goal |
Optimize healthcare systems |
Improve patient-specific care outcomes |
|
Regulatory Pressure |
Moderate |
High; must meet clinical safety and performance standards |
Where Clinical AI Makes the Biggest Impact
So, where does Clinical AI really show its value?
Not in administrative dashboards. Not in billing automation.
It’s at the heart of patient care.
And nowhere is that clearer than in orthopedics, where every angle, measurement, and millimeter can define the success of a surgery.
Let’s break it down.
From 2D Imaging to 3D Understanding
Medical imaging is central to diagnosis and planning. But traditional radiographs often limit the surgeon to two-dimensional views of three-dimensional problems. That’s where Clinical AI changes everything.
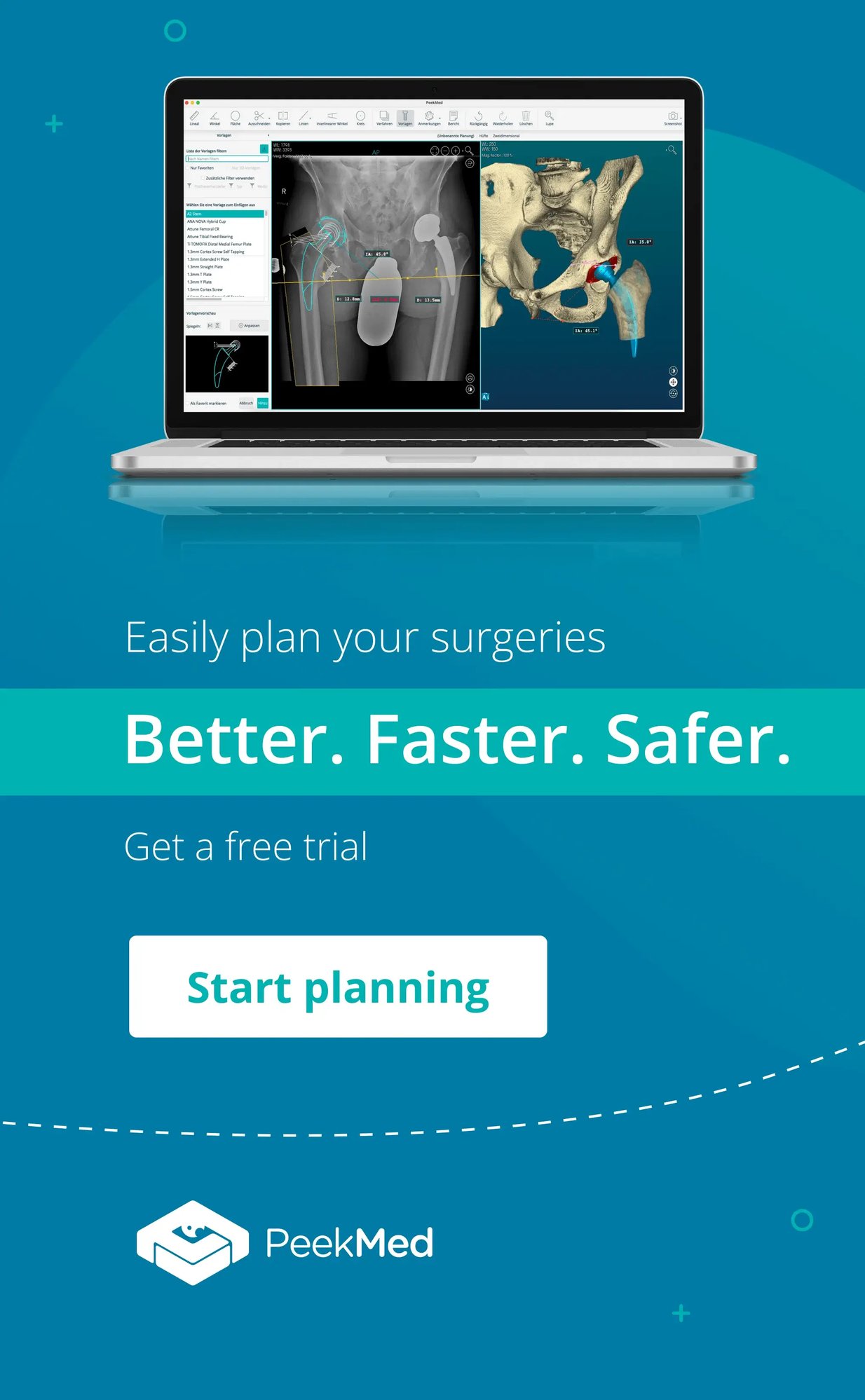
AI-driven platforms like PeekMed allow surgeons to transform 2D X-rays into accurate 3D bone models, giving you a virtual reconstruction of the patient’s anatomy.
You’re no longer estimating angles from flat images—you’re interacting with a lifelike model you can rotate, measure, and plan on.
Radiology and Imaging Diagnostics
Radiology has been at the forefront of Clinical AI adoption. Algorithms trained on thousands of scans can now detect abnormalities in X-rays, MRIs, and CT images faster—and in some cases, more accurately—than human readers alone.
This doesn’t replace the radiologist; instead, it augments them. By identifying potential issues early and flagging edge cases, AI provides clinicians with more time and insights to focus on interpretation and treatment.
Patient-Specific Surgical Simulation
No two patients are the same, and neither should their surgical plans be.
Clinical AI enables surgeons to simulate various approaches before the operation even begins. With PeekMed’s AI-powered platform, you can:
- Test different osteotomy strategies;
- Visualize implant options in a real anatomical context;
- Adjust alignments and angles with live feedback.
This level of personalization reduces variability, improves precision, and shortens operating time.
Enhanced Decision-Making and Surgical Confidence
Clinical AI also enhances diagnostic interpretation and decision confidence. Rather than spending hours comparing templated measurements or calculating by hand, AI automates these tasks—highlighting deviations, suggesting corrections, and giving you more time for high-level surgical planning.
This isn’t replacing surgical expertise—it’s augmenting it.
As detailed in our piece on Artificial Intelligence in Surgery, this augmentation leads to:
- More predictable outcomes;
- Fewer intraoperative surprises;
- Better communication with multidisciplinary teams.
The best part? It all fits into your existing workflow.
The Future Is Focused
AI in healthcare is expanding rapidly, but not all applications are created equal.
Clinical AI is where the stakes are highest and the opportunities most powerful.
It’s not about replacing the physician—it’s about enhancing what you do best.
From radiograph to recovery, Clinical AI ensures that every patient plan is more informed, more tailored, and more effective.
So whether you’re exploring new AI solutions or already integrating them into your practice, the question isn’t if Clinical AI will become standard.
It’s how quickly—and how confidently—you’ll make it part of your surgical toolkit.
References
European Commission. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. https://health.ec.europa.eu/ehealth-digital-health-and-care/artificial-intelligence-healthcare_en
Aidoc. What Is Clinical AI? https://www.aidoc.com/learn/blog/clinical-ai/
Limbic. Clinical AI for Mental Healthcare. https://www.limbic.ai/blog/clinical-ai-for-mental-healthcare
Naik N, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: A Review of Its Applications and Impact on Patient Care. PMC. Published 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8285156/
Nature News. AI in Diagnostics: Are We There Yet?. Nature. March 2025. https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-025-00618-x
CNN Health. AI Diagnosing Disease Faster Than Doctors?. CNN. March 2025. https://edition.cnn.com/2025/03/27/health/artificial-intelligence-diagnosis-technology-wellness/index.html
PeekMed. AI in Healthcare https://blog.peekmed.com/ai-in-healthcare
PeekMed. Artificial Intelligence in Orthopedics. https://blog.peekmed.com/artificial-intelligence-in-orthopedics
PeekMed. Data Augmentation in Orthopedics. https://blog.peekmed.com/data-augmentation-orthopedics
PeekMed. Artificial Intelligence in Surgery. https://blog.peekmed.com/artificial-intelligence-in-surgery
PeekMed. AI Converting Radiographs to 3D Bone Models. https://blog.peekmed.com/ai-converting-of-radiographs-to-3d-bone-models