What are DICOM Images? Everything you need to know
As a medical doctor, do you keep bumping into the expression DICOM images (in radiology, especially) and wondering what it is?
If you grew up wanting to be a doctor, after seeing TV shows such as House MD, Scrubs, or Grey's Anatomy you probably expected that your day-to-day involved holding an X-Ray against a backlight.
While this might have sort of happened at some point, this approach is, nowadays, rather obsolete. Everything is possible thanks to DICOM, a technology used in healthcare to enhance how imaging data is stored and transmitted within hospitals and clinics.
Hospitals and clinics have integrated digital health into their routines, whether in computer surgery or as a diagnostic tool.
Thus, this approach eliminated scenarios like the one we’ve just described – we are very sorry if you were disappointed. It’s for the better.
You might think that, just like knowing how the lights go on and off, this knowledge might seem irrelevant to your day-to-day activity.
However, understanding DICOM and having good knowledge of how to use it can bring new tools to your clinical practice.
This article will clarify the information that you have always wondered about – such as what file format is a CT scan –, but also touchpoints like
- What is DICOM in healthcare
- How to use them in your day-to-day clinical practice
- What is the difference between DICOM and PACS
- How this medical imaging technology is helping transform healthcare
What are DICOM images and how it's used?
DICOM means Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine. It refers to the standard file format used to transmit medical images.
When a patient is submitted to a radiology exam, such as a CT Scan, the imaging information is converted into a DICOM file.
This file is a universal format that can be understood by different systems.
From a day-to-day viewpoint, it can be compared to a PDF file. Word processors create documents in PDF files to ensure the information is not messed up when read on a different system – for example, a printer or a different operating system.
So, how is DICOM used? It’s the same principle... Imaging equipment, like CT Scans or MRIs, needs a universal format that can be understood by other types of equipment created by different manufacturers.
However, more than communication between devices, using DICOM brings several advantages to clinical practice.
In the classic format of radiology exams, support information would be attached to a physical folder containing the exam. Digitalization of information is another advantage of DICOM in radiology.
Patient information such as name, identification number, the reason for the exam, and medical report can be attached to the DICOM file.
This reduces drastically both storage costs and how information systems are used. Making it much easier for the clinical data to flow.
A practical example would be that a radiologist can make comments or notes to colleagues on an x-ray. In a matter of seconds, that information can be transmitted to an orthopedic surgeon.
It also ensures that information won’t be lost. Another step toward a paper-free, more sustainable hospital.
However, in communications in medicine, DICOM is not the only player. PACS is an essential part of optimizing the process. How?

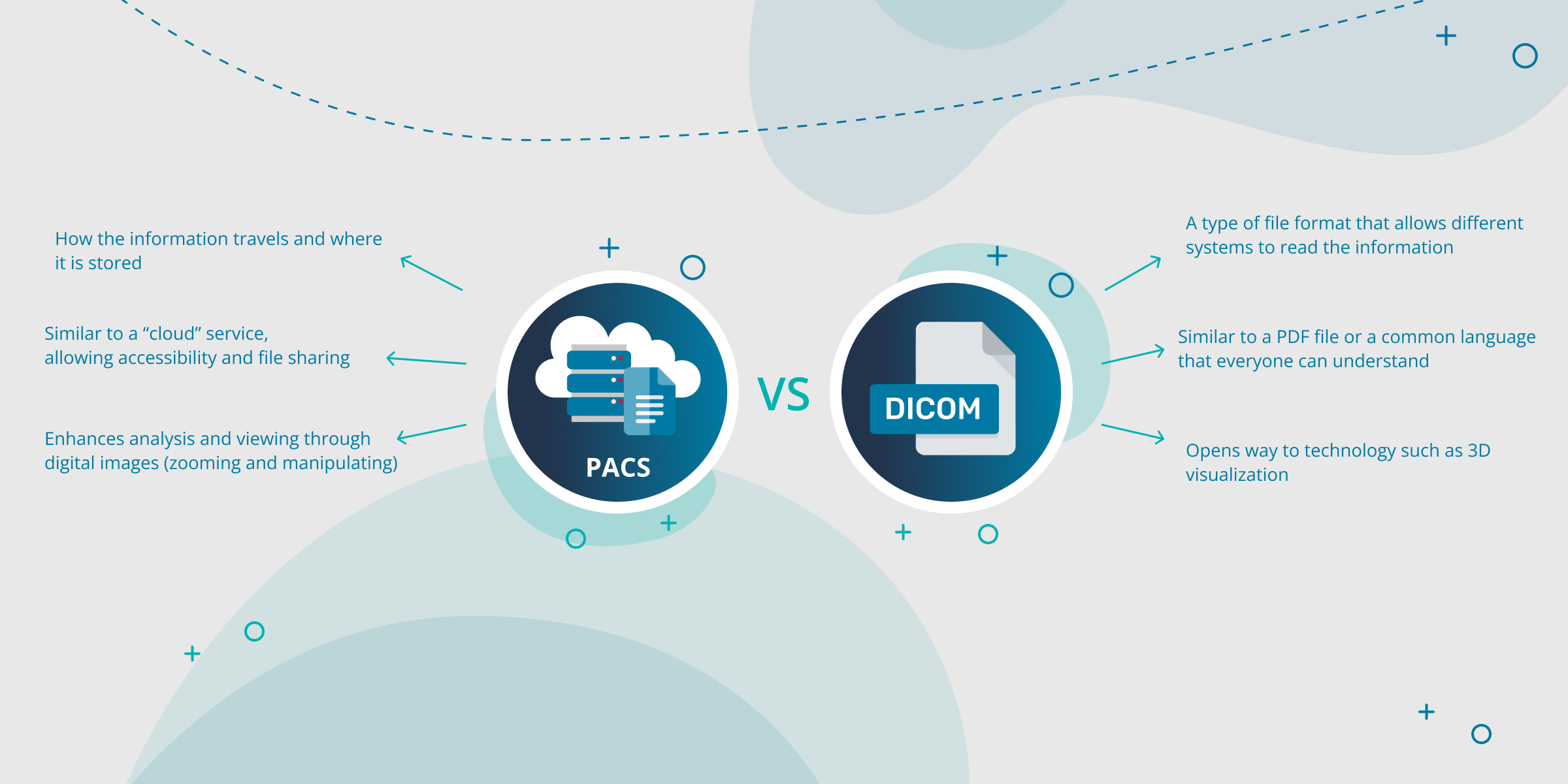
What is the difference between DICOM and PACS?
PACS stands for Picture Archiving and Communication System. It allows for information to be stored and transmitted within a healthcare organization.
Often healthcare professionals try to compare DICOM vs PACS. These, however, are complementary to each other and not competitors. Healthcare institutions can save costs and increase performance by working on how DICOM integrates with PACS.
In short, a PACS Server (or system) is how the information travels and is stored. DICOM files are the “language” used for this process to happen and for different types of equipment to understand each other.
Another practical example would be that two people can talk to each other, but the communication would be optimized if they both speak the same language.
What a DICOM format is in healthcare can be summarized as a universal language between PACS systems.
Combined with PACS, imaging equipment can transfer the patient exam and information directly and instantly to the radiology station for reporting and later, for instance, to the orthopedic surgeon for evaluation.
As such, comparing PACS vs DICOM does not make sense, as they are two parts of a whole.
New Imaging Technologies: how DICOM and PACS are transforming healthcare
Combined with PACS, the use of DICOM brings huge advantages to healthcare.
Integrating DICOM and PACS technology in their imaging systems, healthcare is reducing costs and boosting efficiency – while still opening doors to new clinical technologies such as orthopedic digital templating, in the case of orthopedic surgery.
In the case of orthopedics, PeekMed integrates with all PACS systems.
This allows orthopedic surgeons to access the network, search for a specific patient, and in a matter of seconds import the DICOM files directly into the preoperative planning system.
This is just the tip of the iceberg for the use of Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine combined with other technologies, tho. As we’ve pointed out, Artificial Intelligence uses in healthcare are on the rise and this trend is reaching DICOM, too.

