PeekMed
Computer Assisted-Surgery (CAS) is scaling within the medical field, as technology, AI, and Big Data mature. This is especially true in orthopedics, which is the specialty we will be examining in this article.
While some are already sold on how Computer Assisted-Surgery can be used, there is still some confusion regarding the topic – specifically when it comes to uses and definitions.
In this article, we will explore some common questions on the topic, such as:
What is Computer-Assisted Surgery?
Computer-Assisted Surgery is a broad term that often includes different ideas. Think of it as a concept where technology is used in surgery as a tool to support procedures.
Ultimately, CAS is associated with any surgical procedure that, directly or indirectly uses technology (let’s say a machine or software) together with the surgeon's skills.
This means that different healthcare professionals might have different interpretations of what is computer-assisted surgery. It depends on the type of technology used and the moment when it’s used.
We will explore it further, but before we do, let's continue to study the definition and the goals of CAS.
There may also be some confusion regarding the term used. CAS is often also known as Computer-Aided Surgery, Image-Guided Surgery, Digital Surgery, or Surgical Navigation. All of these are synonymous.
However, as for its goal, one thing is common: Computer-Assisted Interventions aim to improve precision and facilitate minimally invasive approaches.
The main goal is to analyze, evaluate, and perform surgical and therapeutic interventions. This allows surgeons to achieve precise viewing, tracking, positioning, and angling of surgical instruments.
How does Image-Guided Surgery work and how can it be used?
It all starts when using diagnostic imaging, like Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI), or the X-ray.
These are uploaded into a system that, through several scanning methods and image data techniques, provides the surgeon with accurate information about the patient. Often, these are 3D images.
This brings medical image and computing to computer-assisted surgery!
Now it depends on the type of computer-assisted surgery you are dealing with. As for the moment when it’s used, normally these are split as follows:
Types of Computer-Assisted Surgery:
-
Preoperative
-
Intraoperative
-
Postoperative
In preoperative scenarios, Computer Assisted Surgery might mean that you are using the technology to make preoperative planning much easier and more precise. By using this information you are to have a better understanding of what you will find when in surgery.
When it comes to intraoperative, it usually involves exploiting images with information captured by LED cameras. Much like a real-time tracking system of a Car’s Global Positioning System (GPS), but for surgery. In this case, CAS acts as a surgical navigation system.
As for postoperative, CAS allows the surgeon to have a better understanding and in-depth follow-up of the patient. Thus, surgeons can have better insight into recovery.
In Orthopedics, ultimately, this leads to several gains, such as having the correct implant size and instruments ready before the surgery. Thus, you are gaining sustainability and reducing costs, which are huge benefits.
Talking about benefits:
What are the benefits of Image-Guidance?
Image-guided surgery (IGS) is all about having greater control of the surgical procedure.
It is a huge advantage to view 3D models since it allows stereoscopic vision, providing more information for the surgeon.
As we’ve stated, this can be in real-time or before the surgery even begins.
In Orthopedics, 3D imaging allows a more precise choice for the implant size. This makes it easier to visualize the anatomical structures, regardless of the patients’ slight body movements during the scanning process.
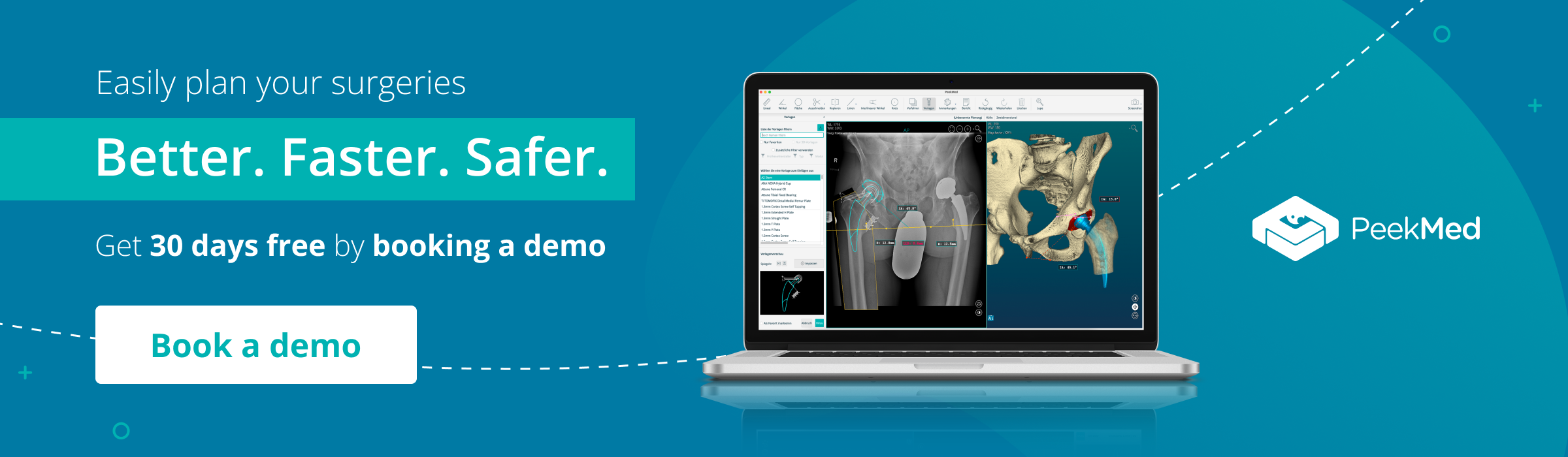
Integrating all these technologies, PeekMed allows the surgeon to use a set of tools that assist to perform easier, faster, and safer plans for these procedures. The system can be used in different types of surgery using a 2D environment, 3D environment, or hybrid.
Combined with Artificial Intelligence, our solution offers tools such as automatic bone segmentation and automatic templating, too. These allow the surgeon to speed and automatize several steps that, normally, are quite time-consuming.
Other than that, it is important to highlight that this approach may lead to better surgical care.
Ultimately, it will allow the surgeon to reduce the level of invasiveness of surgery, too, thanks to robotic surgery.
Thus surgical robotics it will be possible to more precisely prepare bone and place implants with the goals of improving recovery, reducing complications, and obviating the need for expensive revision procedures. Robotic-assisted surgery represents an evolution of CAS and can be viewed as an adjunctive tool to improve a physician’s ability to perform the procedure.
This is leading to a new generation of implants and surgical tools, often powered by 3D Printing Solutions.
Is Computer-Assisted Surgery only used during surgery?
By now, you are probably aware that Computer-Assisted Surgery can start even before the surgery, with preoperative planning.
This includes choosing what implants will be needed, how the procedure will be performed and also helps anticipate possible problems that may occur during the surgery.
But why is preoperative planning so important?
Combining AI with surgical planning, the surgeon automates procedures that can be missed either due to attention or because it is too small. Thus, error probability is drastically reduced, making it safer for the patient while still saving time.
Assisted Interventions lead to more accuracy
Accuracy is the major concern when it comes to using image-guided techniques.
However, when it comes to precision, most studies have demonstrated greater accuracy with computer guidance.
On that note, a scientific paper suggests that by using PeekMed surgeons can avoid over/under corrections and joint line obliquity. This leads to the best outcome possible for each patient, individually.
Globally, Artificial Intelligence added a lot of value to orthopedics and improved other orthopedic technologies. And these solutions ain't something that only a few can use – it's a solution available to anyone.